Supplier failures cost money and credibility. Defective materials, failed audits, and missed deliveries expose weak supplier oversight.
Supplier management tools should stop these problems early, not just log them after damage occurs. Yet many platforms focus on spend or sourcing and leave supplier quality unchecked.
That gap leads to recalls, rework, and compliance findings that teams struggle to close.
In this article, you’ll see how the top seven supplier management tools compare and which ones stop supplier issues before they affect your operation.
TL;DR
Here are the top seven supplier management tools for procurement:
- TLM
- Ivalua
- SAP Ariba
- Coupa
- GEP SMART
- Precoro
- Esker
What Are Supplier Management Tools Used For?
Supplier management tools help procurement and quality leaders manage suppliers from initial approval to risk review.
They replace manual follow-ups with one system that records what suppliers submit, how they perform, and where problems show up.
Supplier management software is used to:
- Onboard suppliers and collect required documentation
- Store supplier data and manage contracts
- Track supplier performance against clear requirements
- Record audits, inspections, and nonconformances
- Assign corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs) and track closure
These tools also support supplier risk management. Procurement and compliance teams review quality issues, audit results, and supplier history without switching between systems.
Most platforms include a supplier portal where suppliers upload documents, respond to findings, and confirm corrective actions. That keeps procurement processes consistent across the supplier lifecycle.
Top 7 Supplier Management Tools Worth Checking Out
Most supplier management tools handle purchasing or payments. Very few manage supplier quality and risk under audit and production pressure.
Below is a comparison of the top seven supplier management tools to help you choose a solution that holds suppliers accountable.
1. TLM

Total Lean Management (TLM) focuses on supplier quality management and compliance management for organizations operating under International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 9001 and ISO 13485.
It manages supplier records alongside audits, inspections, nonconformances, and corrective actions. Supplier activity stays documented and traceable within one supplier management system.
This supplier management software treats supplier performance as an operational requirement. Procurement and quality leaders review outcomes tied to materials, inspections, and corrective actions.
That foundation supports supplier performance management and third-party risk management through documented results.
Key Features
- Customizable supplier approval levels with automated expiration alerts
- Supplier onboarding tools tied to approval and qualification workflows
- Supplier audits with configurable templates and scorecards
- Supplier performance tracking through inspection and audit results
- Nonconformance and CAPA workflows linked to supplier records
- Supplier web portal for supplier corrective action request (SCAR) responses
- Dashboard alerts for overdue reviews, approvals, and actions
- Centralized supplier information and contract management
- Integration with inventory, purchase orders, inspections, and audits
How TLM Tracks Supplier Performance
TLM tracks supplier performance through inspection results, audit findings, and nonconformance history.
Performance monitoring highlights repeat issues and unresolved actions. Procurement operations evaluate supplier performance using performance metrics tied to quality assurance (QA).
Risk monitoring reflects supplier behavior documented across audits, inspections, and corrective actions. Each outcome updates the supplier record.
That history supports informed decisions for critical suppliers and early identification of quality or financial risk.
Supplier Collaboration With Accountability
TLM supports supplier collaboration through a secure supplier portal. Suppliers submit documents, respond to findings, and complete corrective actions inside the system.
Each response remains linked to the supplier record, which improves data accuracy and accountability across supplier interactions.
One System for the Entire Supplier Lifecycle
TLM manages suppliers throughout the entire supplier lifecycle, from supplier onboarding through ongoing performance monitoring.
It connects supplier management processes with inventory, inspections, audits, and purchasing workflows.
Quality management remains connected to procurement decisions throughout.
2. Ivalua
Image source: ivalua.com
Ivalua is procurement software used by large organizations with complex source-to-pay requirements.
The platform centralizes supplier information and connects it to sourcing, contract management, purchasing, and invoicing.
Its supplier management capabilities focus on supplier relationship management, collaboration, and performance programs rather than inspection-driven quality control (QC).
Procurement teams use Ivalua to onboard new suppliers, validate supplier information, and manage approval workflows.
Supplier evaluation relies on scorecards, surveys, and external data to track vendor performance and supplier risk.
Risk monitoring spans suppliers, sub-tiers, and contracts, which supports supply chain management and sourcing decisions for large supplier bases.
Key Features
- Centralized supplier information management across the source-to-pay process
- Supplier onboarding with data collection, validation, and approval workflows
- Supplier evaluation using scorecards, surveys, and performance metrics
- Risk monitoring at supplier, sub-tier, and contract levels
- Supplier portal for collaboration and issue tracking
- Integrated sourcing, contract management, purchasing, and invoicing
Pros
Ivalua supports strategic sourcing and supplier relationship management across complex procurement operations.
Its configurability is helpful for procurement leaders who need supplier management tied closely to contracts, spend analysis, and financial data.
Cons
Ivalua relies on assessments and performance metrics rather than inspection-level quality management. That limits risk mitigation for organizations that need to monitor nonconforming materials.
Implementation and ongoing configuration require significant planning and technical effort, especially in enterprise environments.
3. SAP Ariba
Image source: sap.com
SAP Ariba is used by large procurement organizations to manage supplier information, lifecycle stages, performance, compliance, and risk across the source-to-pay process.
The platform centralizes supplier data and shares it across sourcing, purchasing, and invoicing. Procurement teams work from one consistent record.
SAP Ariba manages supplier onboarding, qualification, and segmentation through configurable workflows.
Suppliers maintain their own profiles through the SAP Business Network. That keeps vendor information accurate and reduces manual updates.
Procurement teams rely on this centralized data to support sourcing decisions and daily procurement workflows.
Key Features
- Supplier data shared across the source-to-pay process
- Automated supplier onboarding, qualification, and segmentation
- Supplier self-service portal through SAP Business Network
- Supplier performance and compliance monitoring
- Supplier risk due diligence using third-party data and alerts
- Two-way synchronization with SAP enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
Pros
SAP Ariba handles large vendor ecosystems and keeps supplier data consistent across sourcing, purchasing, and invoicing.
Procurement teams get defined workflows for onboarding, qualification, and ongoing monitoring. Compliance and risk signals stay visible throughout procurement activities.
Cons
SAP Ariba doesn’t manage supplier quality at the inspection or material level, so it can’t stop nonconforming materials before receipt.
Many users report that everyday tasks require too many clicks, which slows work, frustrates occasional users, and makes training more demanding.
4. Coupa
Image source: coupa.com
Coupa frames supplier management around spend, invoicing, and third-party risk. It puts heavy emphasis on onboarding speed, invoice accuracy, and automated risk detection.
Supplier interactions run through the Coupa Supplier Portal. Suppliers update information when they receive a purchase order or submit an invoice.
The system blocks incomplete invoices and triggers alerts automatically. That cuts manual follow-up and keeps supplier data usable for accounts payable automation.
Risk monitoring relies on data and automation. Coupa scans external sources, community data, and user feedback. It tracks risk across information security, anti-bribery and corruption, data privacy, and regulatory exposure.
When risk ratings change, the platform recommends actions such as pausing a supplier or reviewing alternatives. Procurement teams can respond faster to compliance issues and financial instability.
Key Features
- Supplier self-service portal for purchase order and invoice updates
- Automated third-party risk detection across multiple compliance domains
- Artificial intelligence-driven risk alerts with recommended actions
- Supplier risk and performance monitoring in one interface
- Invoice validation with automatic warnings and submission blocks
- Supplier diversity tracking and reporting
Pros
Coupa reduces manual effort across supplier onboarding, invoicing, and risk monitoring. Procurement teams see supplier risk and performance next to purchasing and payment activity, which keeps finance and procurement in sync.
Cons
Coupa doesn’t manage supplier quality at the material or inspection level. That makes it harder to stop nonconforming materials before receipt.
Many users describe the interface as dated and navigation-heavy, which slows invoice processing and frustrates vendors.
5. GEP SMART
Image source: gep.com
GEP SMART focuses on supplier data, performance, and risk across the source-to-pay lifecycle. Its foundation is Supplier Master Data Management.
The platform integrates with existing enterprise systems, including ERP, supplier relationship management (SRM), and sourcing tools.
It cleans and normalizes supplier master data, compares records against the GEP SMART Vendor Master, and removes duplicates. Records stay updated through real-time and batch processing.
Supplier evaluation and oversight sit on top of that data. Procurement teams collect information through forms, scorecards, surveys, and questionnaires.
They track key performance indicators (KPIs) and service-level agreements (SLAs), then review reports to confirm which suppliers meet requirements. Action plans and assigned stakeholders support ongoing supplier engagement.
Key Features
- Supplier Master Data Management with cleansing, normalization, and duplicate removal
- Integration with ERP, SRM, and sourcing tools to create and update supplier records
- Real-time and batch processing for supplier master data updates
- Supplier scorecards, surveys, and questionnaires for supplier evaluation
- Reporting and analysis to identify suppliers that meet requirements
- Supplier status flags, such as preferred, qualified, or blacklisted
Pros
GEP SMART prioritizes accurate vendor information across multiple systems. It keeps supplier records updated and supports supplier evaluation with scorecards and reporting.
Cons
GEP SMART emphasizes supplier data management and performance tools, not inspection-driven quality controls. Users also report slower performance with large data volumes and cluttered dashboards.
6. Precoro
Image source: precoro.com
Precoro is a supplier management tool that focuses on day-to-day procurement execution rather than supplier risk or quality programs.
It’s commonly used as vendor management software for handling requests, approvals, purchase orders, invoices, and budgets.
Procurement teams use Precoro to automate routine workflows. Purchase requests move through approval chains, convert into purchase orders, and remain linked through receipt and payment.
Precoro also supports supplier coordination through its Supplier Portal. Vendors submit documents, update catalogs, receive purchase orders, and send invoices within the system.
Automated invoice capture and three-way matching flag duplicates or mismatches before they reach finance.
Key Features
- Request-to-purchase-order automation
- Invoice capture with optical character recognition and three-way matching
- Duplicate and missing-data invoice checks
- Budget tracking during requests and approvals
- PunchOut catalogs
- Inventory tracking
- Custom reports with Excel export
Pros
Precoro keeps supplier management and purchasing activity organized from request through payment. Approval workflows reduce off-contract buying.
The Supplier Portal cuts manual follow-ups for documents, catalogs, and invoices. Users often mention the interface as easy to learn.
Cons
Precoro doesn’t manage supplier quality, inspections, or corrective actions, so teams rely on separate tools for those controls.
Organizations with multiple subsidiaries often manage approvals separately by entity.
PunchOut catalog support includes fewer vendors than larger procurement suites, which can restrict catalog-based purchasing options.
7. Esker
Image source: esker.com
Esker is a supplier management tool for supplier relationship management and risk management. It uses procurement automation for standardized workflows, automated supplier onboarding, and supplier performance tracking.
Suppliers submit legal documents and update supplier information through a self-service portal. Esker also supports onboarding questionnaires and checks the taxpayer identification number (TIN) for compliance.
Esker also addresses supplier inquiries for accounts payable (AP) and procurement teams. Its GPT-powered inquiry management analyzes, categorizes, and drafts responses to supplier questions.
The platform screens suppliers against politically exposed persons and sanction lists, performs Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) checks, and automates bank verification to maintain accurate supplier records.
Key Features
- Automated supplier onboarding with questionnaires and document collection
- Supplier self-service portal for data updates and certifications
- Compliance monitoring with alerts for expiration and noncompliance
- Supplier performance tracking with dashboards and KPIs
- GPT-powered supplier inquiry management for AP and procurement
- Sanction list, politically exposed person, and OFAC screening
- Bank account verification automation to reduce fraud risk
Pros
Esker combines supplier onboarding, compliance monitoring, supplier performance tracking, and inquiry management in one management platform.
It supports risk screening, certification tracking, and bank verification for the most critical suppliers.
Cons
Users report dense payment processing screens and frequent handoffs during approvals. Some also note limits on handling multiple tasks within the same approval flow.
Evaluate Supplier Risk Through Audits and Inspections With TLM
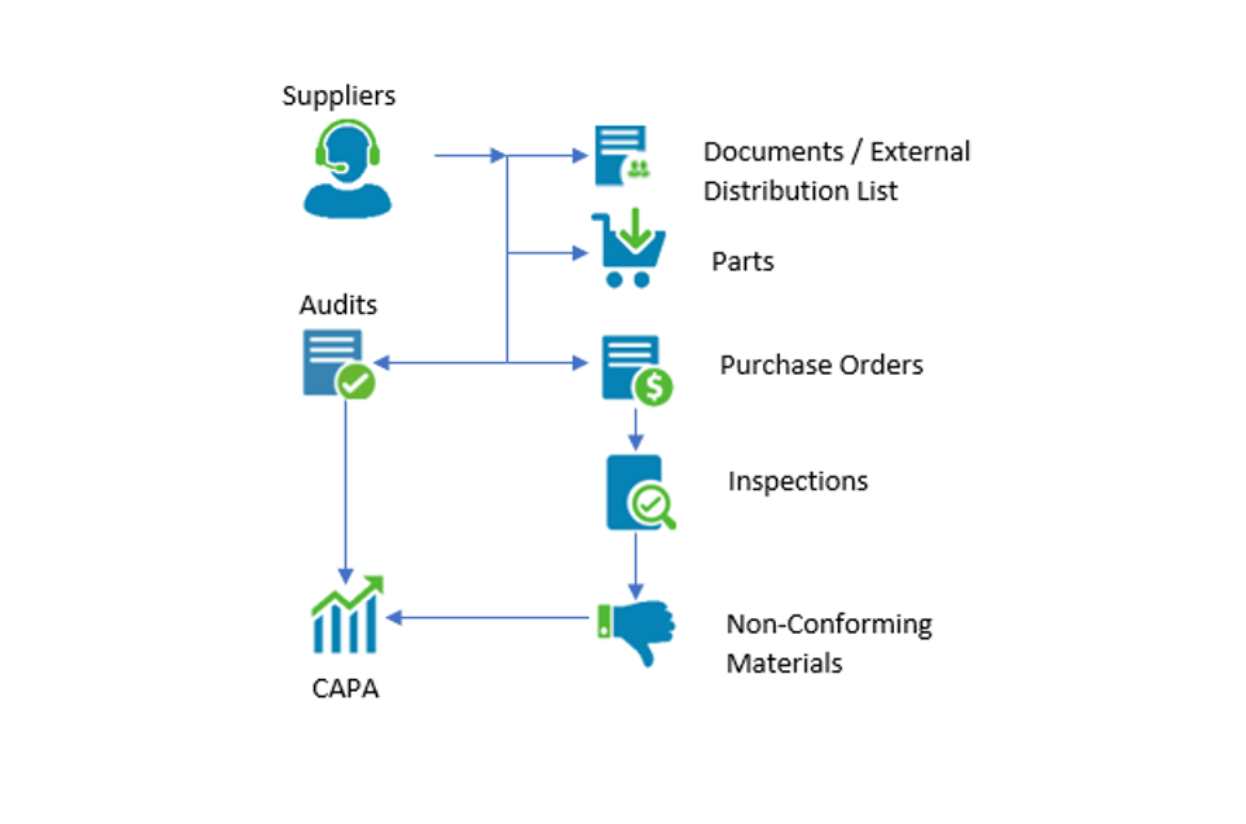
Most supplier management tools stop at supplier data. They store profiles, contracts, and scores, then hand execution off to existing procurement systems.
That setup supports sourcing and spend tracking. It doesn’t stop nonconforming materials from reaching production. Inspections, quality checks, and corrective actions usually happen after an issue shows up.
That delay introduces risk. Procurement-first platforms help maintain vendor relationships, but they don’t cover what auditors and production teams review first.
A supplier management system should influence how suppliers perform, not just log what already happened.
TLM takes a different position. Audits, inspections, nonconformance reports, and CAPAs run in the same system as supplier records.
Quality activity doesn’t sit downstream from procurement. It happens as materials move through receipt, inspection, and resolution.
Automation keeps every supplier event documented and traceable from start to close. Decisions rely on evidence, which leads to more consistent outcomes.
That distinction matters in ISO- and FDA-regulated environments. In those settings, supplier management software becomes part of procurement strategy, not a reporting add-on.
FAQs About Supplier Management Tools
What are the four key elements of supplier management?
Supplier management typically covers supplier onboarding, performance monitoring, risk and compliance oversight, and ongoing supplier relationships.
These elements determine how suppliers enter your organization, how they perform, and how issues get addressed.
What is the best SRM tool?
The best supplier relationship management (SRM) tool depends on what problems you need to solve. Some SRM tools focus on supplier data and collaboration, while others handle risk, quality, or compliance.
When evaluating options, key features to look for include automation capabilities and how well the tool helps improve vendor relationships in daily operations.
What are the five Ps of procurement?
The five Ps of procurement usually refer to Purpose, Process, People, Performance, and Partnerships.
Together, they explain how procurement supports business goals and manages suppliers effectively.
Strong supplier management tools reinforce these areas by supporting stronger supplier relationships instead of relying on manual follow-ups.
What are the different tools for SCM?
Supply chain management (SCM) tools include systems for sourcing, procurement, supplier management, inventory, and logistics.
Supplier management tools focus on suppliers themselves, such as performance, risk, and compliance.
The most effective setups connect these tools with existing systems so supplier decisions support the entire supply chain.






 Demos
Demos